Installing Docker on Puppy Linux Trixie Wayland: The Complete Survival Guide
Installing Docker on Puppy Linux (specifically the new Trixie Wayland version) is not for the faint of heart. Since Puppy runs in RAM and uses a layered filesystem, a standard Docker installation often leads to a filled-up save file, connection errors, or disk usage explosions due to incompatible storage drivers.
I recently went through the pain of setting this up so you don’t have to. Here is the definitive guide to running Docker Engine (and VS Code Dev Containers) on Puppy Linux Trixie Wayland.
Prerequisites
Before we start, you must understand that Puppy’s default RAM-based storage is insufficient for Docker.
- An Ext4 Partition: You need a dedicated partition on your hard drive (HDD/SSD). Do not use FAT32 or NTFS, as Docker requires Linux file permissions.
- In this guide, I will assume your Ext4 partition is mounted at
/mnt/sda4.
- In this guide, I will assume your Ext4 partition is mounted at
- Kernel Check: Ensure your kernel supports OverlayFS (most modern Puppy kernels do).
Install Docker via APT
Since Trixie is based on Debian, we can use apt. Open your terminal:
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Update repositories
pkg get-repo-files
apt update
# Install Docker
apt install docker.io
Stop! Do not run any containers yet. If you do, Docker will default to using your RAM (SaveFile) for storage, which will crash your session within minutes.
Preparing the Storage
We need to redirect Docker’s heavy data (images, containers, volumes) to your hard drive partition (sda4) to keep your Puppy RAM usage low. Create a dedicated directory structure on your HDD:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Create a folder for Docker data
mkdir -p /mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/docker
# Create a folder for Temp files (Crucial for VS Code Dev Containers)
mkdir -p /mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/tmp
# Grant permissions
chmod 777 /mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/tmp
Configuring the Daemon
This is the most important step. We need to create a daemon.json file to solve three major problems at once:
- Storage Location: Pointing to sda4.
- Storage Driver: Forcing overlay2. By default, Puppy might fallback to vfs, which duplicates data and can turn a 2GB image into 29GB of disk usage.
- DNS Networking: Fixing the Could not reach host errors inside containers.
Create or edit the configuration file:
geany /etc/docker/daemon.json
Paste the following configuration:
1
2
3
4
5
{
"data-root": "/mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/docker",
"storage-driver": "overlay2",
"dns": ["8.8.8.8", "1.1.1.1"]
}
Note: If Docker fails to start with overlay2, verify your kernel supports it with cat /proc/filesystems | grep overlay. If absolutely necessary, install fuse-overlayfs and use that driver instead.
Network Fixes
Debian Trixie uses nftables by default, but Docker prefers iptables-legacy. If you encounter network issues (containers cannot ping the outside world), run these commands to switch alternatives:
1
2
update-alternatives --set iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy
update-alternatives --set ip6tables /usr/sbin/ip6tables-legacy
Also, ensure IP forwarding is enabled:
1
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Start Docker
Now you can safely start the service.
1
2
3
4
5
# Stop any running instance
service docker stop
killall dockerd
service docker start
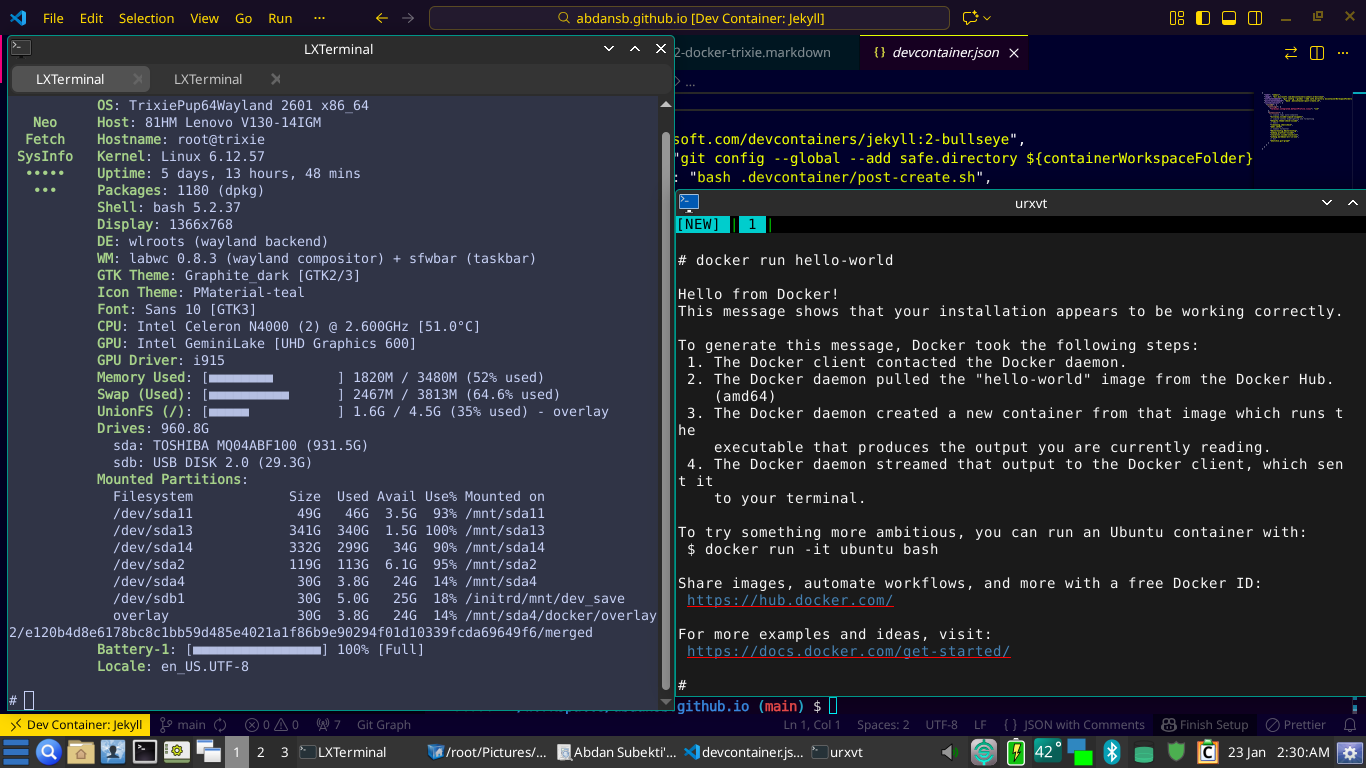
Verify that Docker is using the correct driver and path:
1
docker info | grep -E "Storage Driver|Docker Root Dir"
Output should show overlay2 and /mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/docker.
Running VS Code Dev Containers
If you are using VS Code Dev Containers, the build process often extracts huge files to /tmp, which is in RAM. This causes “No space left on device” errors during build. To fix this, launch VS Code from the terminal with a custom TMPDIR pointing to your hard drive:
1
2
export TMPDIR=/mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/tmp
code --no-sandbox --user-data-dir=/mnt/sda4/Puppy_Data/vscode_data
Conclusion
You now have a fully functional Docker environment on Puppy Linux Trixie Wayland that:
- Doesn’t eat up your RAM/SaveFile.
- Uses efficient storage drivers (overlay2).
- Has working DNS resolution.
Happy coding on your lightweight distro!